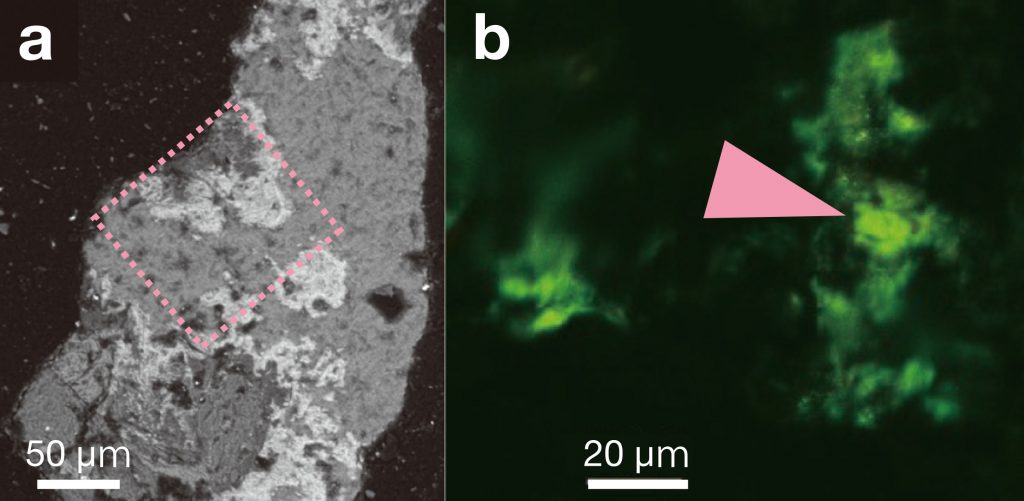
Life on Mars: Search deeper!
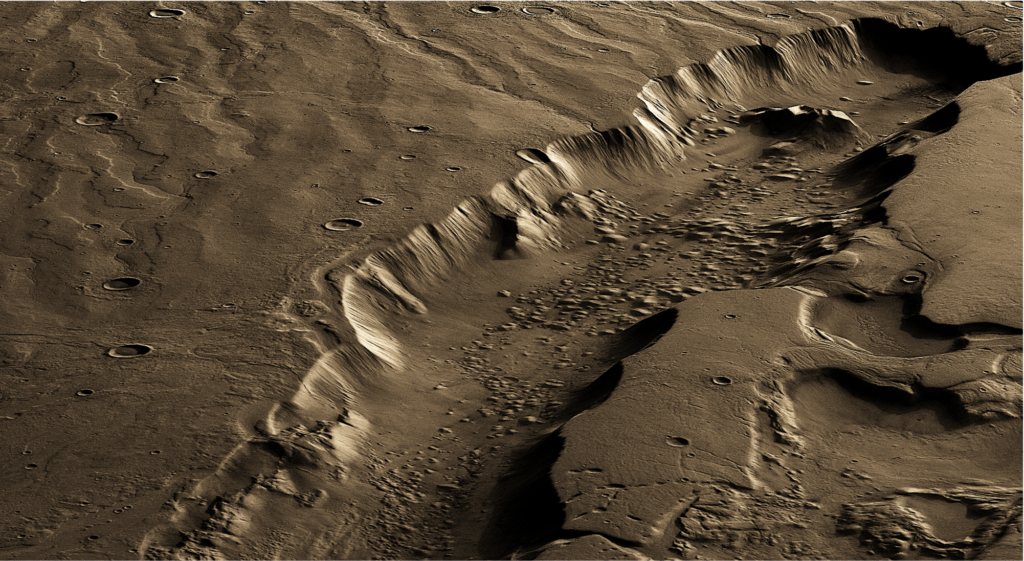
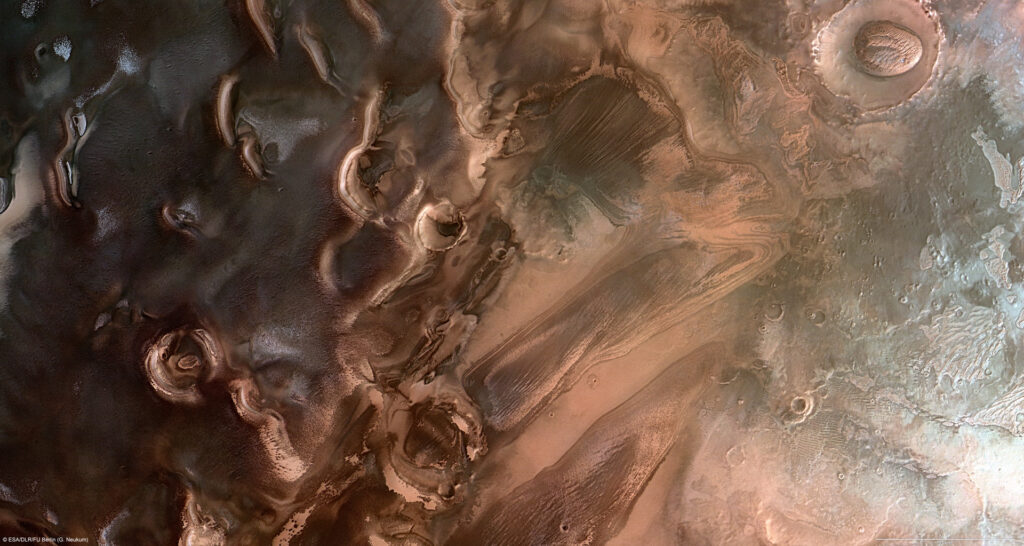
Has Mars ever had a surface that is friendly to life? Planetary scientists are struggling to find enough remnants of a former atmosphere. Even if one considers that Mars may have lost a large part of its oxygen and water to space, gaps remain - even for the past. On the other hand, there are of course the valleys, dry waters and river systems still visible today, into which water would have had to have flowed billions of years ago. And if the water on the surface was not frozen, the temperatures must have been pleasant. Even if this…